Google is one of the most influential companies in the world. Its products and services have become a part of our daily lives. The company’s stock price reflects its success, and many investors want to invest in Google. However, there are two different stock tickers for Google: GOOG and GOOGL. This article will explore the differences between GOOG vs GOOGL, and help you understand which is the right choice.
What are GOOG and GOOGL?
GOOG and GOOGL are the two stock tickers for Alphabet, Google’s parent company. Alphabet was created in 2015 as a holding company for Google and its various other subsidiaries. The company has two classes of stock: Class A and Class C. Class A shares are represented by the ticker symbol GOOGL, while Class C shares are represented by the ticker symbol GOOG.
What is the difference between GOOG and GOOGL?
The primary difference between GOOG and GOOGL is that they represent different classes of stock. GOOGLE represents Class A shares, while GOOG represents Class C shares. Class A shares come with voting rights, while Class C shares do not.
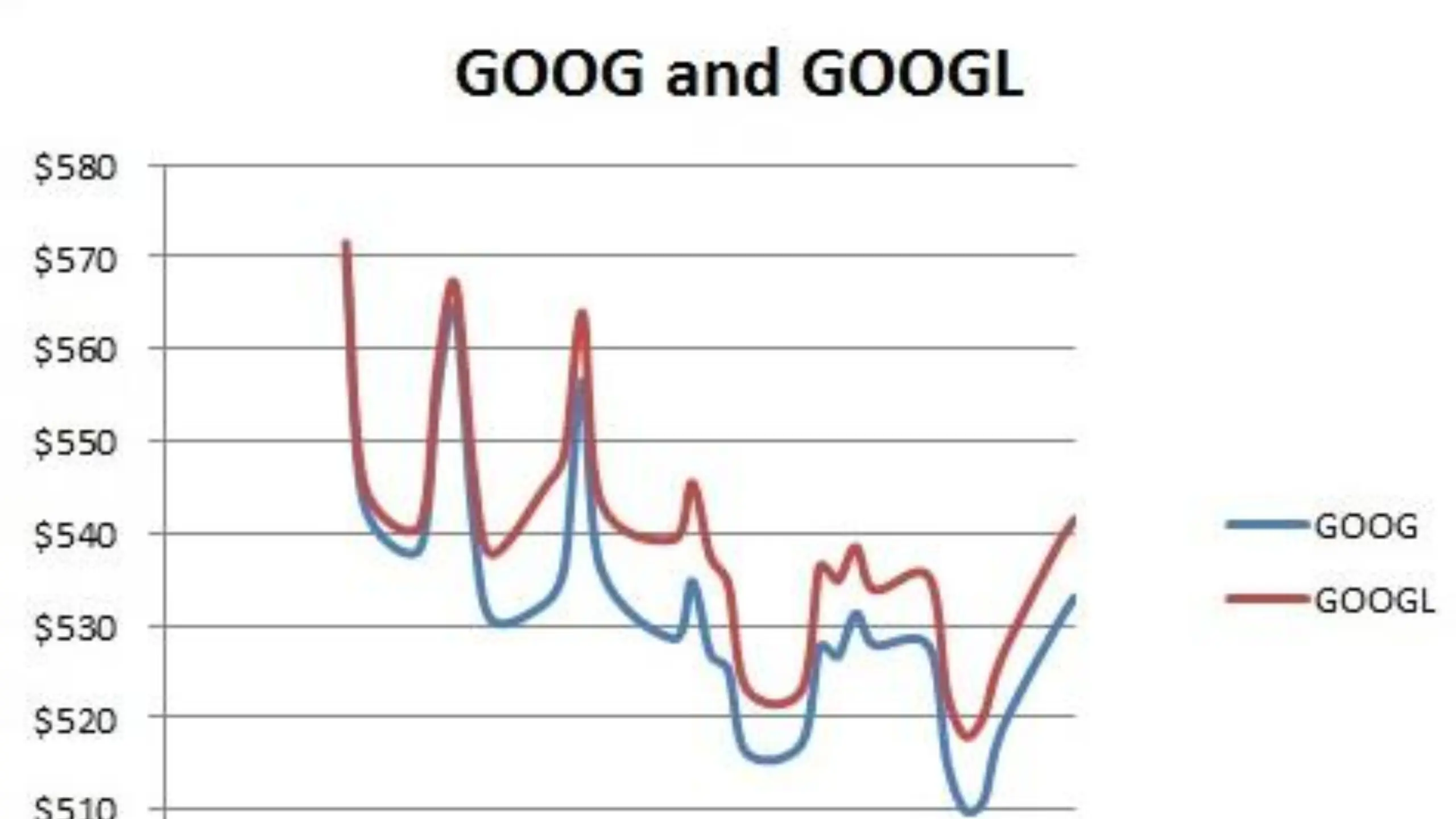
Another important difference between the two classes of stock is the way they are priced. Class A shares tend to trade at a higher price than Class C shares because they come with voting rights. This means that investors who purchase Class A shares have more say in the company’s decisions. And are entitled to receive a higher percentage of the company’s profits.
Which class of stock is right for you?
Deciding which class of stock to invest in depends on your investment goals and preferences. If you are looking for more control over the company’s decisions, Class A shares may be the better choice for you. On the other hand, if you are more interested in the company’s financial performance. They don’t care about voting rights, Class C shares may be the better option.
It is also worth noting that some investors prefer to invest in index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). That track the performance of the entire stock market. If you are one of these investors, you will likely end up owning both GOOG and GOOGL shares, as they are both included in many of these funds.
Ownership Structure
Google’s ownership structure is unique in that it has two classes of stock, with different voting rights. Class A shares have one vote per share, while Class C shares have no voting rights. The company’s founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, and its executive chairman, Eric Schmidt. They hold a large number of Class B shares, which have 10 votes per share. This gives them a significant amount of control over the company’s decisions. They despite owning a relatively small percentage of the company’s overall shares.
Price Difference
As mentioned earlier, Class A shares tend to trade at a higher price than Class C shares because they come with voting rights. This means that the two classes of shares can have different prices, even though they represent ownership in the same company. For example, as of April 3, 2023, GOOG was trading at $3,061.23 per share, while GOOGL was trading at $3,120.54 per share.
Dividend Policy
Google has never paid a dividend on its common stock. This is because the company has traditionally reinvested its profits into research and development. It has focused on long-term growth rather than returning cash to shareholders. However, in 2021, Alphabet announced that it would begin paying a dividend on its Class C shares. They start with a quarterly payment of $0.16 per share. The company has not indicated whether it plans to pay a dividend on its Class A shares.
Tax Implications
From a tax perspective, there is no difference between owning GOOG or GOOGL shares. Both classes of stock represent ownership in the same company and any capital gains. The losses will be calculated based on the price you paid for the shares and the price you sell them for. However, if you hold shares of both classes, you will need to keep track of your cost basis separately for tax purposes.
Institutional Ownership
Institutional investors, such as mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds, own a significant percentage of Google’s outstanding shares. As of December 31, 2021, institutional ownership of GOOG was 76.19%, while institutional ownership of GOOGL was 78.34%. This means that most of the trading activity in Google’s stock is driven by large, professional investors, rather than individual retail investors.
Historical Context
In 2014, Google announced that it would create a new holding company, called Alphabet. As part of this restructuring, Google’s common stock was converted into two classes of stock: Class A and Class C. The Class A shares were given the ticker symbol GOOGL, while the Class C shares were given the ticker symbol GOOG.
The creation of Alphabet was seen as a way for Google to better focus on its core businesses. Such as search, advertising, and Android, while also allowing it to invest in new, innovative projects. Alphabet’s various subsidiaries include Google, YouTube, Waymo (a self-driving car company), and Verily (a life sciences company), among others.
Investor Activism
In recent years, some investors have become increasingly critical of Google’s dual-class stock structure. It argues that it gives too much power to the company’s founders and insiders. In 2017, a group of shareholders sued Alphabet, alleging that the companies. The board of directors had breached their fiduciary duties by allowing the founders to maintain control of the company through their ownership of Class B shares.
Final Analysis:
GOOG vs GOOGL are two different stock tickers for Alphabet, Google’s parent company. GOOGLE represents Class A shares, which come with voting rights. While GOOG represents Class C shares, which do not. Deciding which class of stock to invest in depends on your investment goals and preferences. As well as other factors such as price differences, tax implications, and historical context. Regardless of which class you choose, investing in Google can be a lucrative opportunity for long-term growth. But investors should carefully consider the risks involved.